An upsell funnel guides customers through a sequence of offers that encourage them to purchase additional or higher-value items, often with just one click.
Instead of ending the sale after one product, an upsell funnel moves your customer to buy more, like relevant upgrades, bundles, or add-ons, at the moment they’re most likely to say yes.
In this blog, we’ll explain what upsell funnels are, how they work, how to create an upsell funnel, and practical examples to increase order value without annoying your customers.
Increase your average order value quickly by creating upsell and cross-sell campaigns using UpsellWP.
What is an Upsell Funnel?
An upsell funnel is a marketing sequence where, after a customer makes a purchase (or commits to one), they are presented with additional offers to buy more or upgrade their purchase.
Instead of ending the sale at the first product, an upsell funnel extends the customer journey with relevant extra offers.
The goal is to increase the customer’s average order value (AOV) and overall satisfaction by helping them discover more value.
An upsell funnel often works like this:
- A customer selects a product and begins checkout.
- Once they’ve entered payment details and clicked “Buy,” they immediately see another offer (the upsell) on the next page before they see a final thank-you.
- The customer can accept with a single click (no need to re-enter payment info) or decline the offer.
Difference Between Upsell vs. Cross-sell:
It’s worth noting the difference between an upsell and a cross-sell, since both can appear in an upsell funnel.
An upsell typically means offering a higher-end or enhanced version of the product (or adding a warranty, subscription, etc.).
A cross-sell suggests a different product that complements the original purchase (like offering a phone case when someone buys a phone).
For example, “Would you like to supersize your meal?” is an upsell (upgrading to a bigger size), while “Would you like fries with that?” is a cross-sell (adding a complementary item).
Upsell funnels can include both types of offers in sequence. In fact, many e-commerce upsell funnel tools allow a “true upsell” first, followed by cross-sells.
How Upsell Funnels Work?
- Upsell funnels rely on simple conditional flows.
- Using branching logic, you can set up a series of offers that display depending on the customer’s response to the previous offer.
- For instance, if the customer accepts Offer A, they get shown Offer B next; if they decline Offer A, the funnel might skip ahead or show an alternative Offer C (often a cheaper downsell offer).
- After one or two upsell attempts, the funnel ends at a final thank-you page.
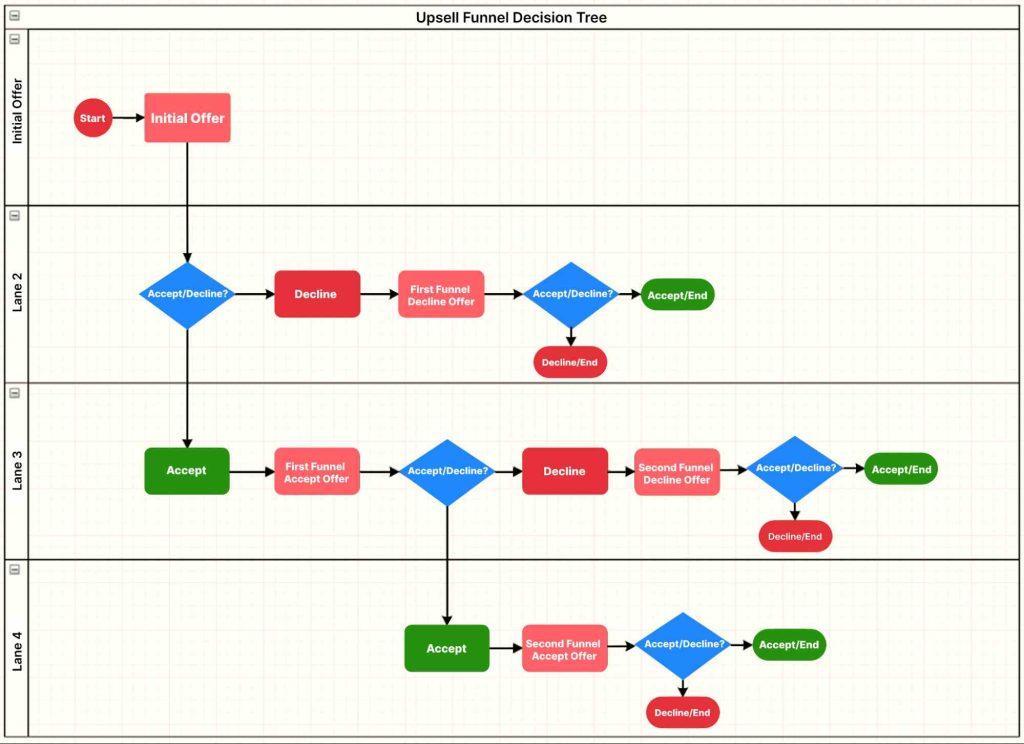
This process is visualized in the flowchart below, which illustrates a basic upsell funnel decision tree with accept/decline branches:
Upsell funnel decision flow: A customer sees an initial offer, then conditional upsell offers based on whether they accept or decline. This branching ensures the customer isn’t overwhelmed, and each offer is a logical next step.
Next, let’s explore why these funnels are so important for your business.
How to Create an Upsell Funnel (Step by Step)
Creating an upsell funnel might sound complex, but it can be broken down into clear steps.
Here’s how to build an upsell funnel:
1. Choose the Right Upsell Offer
Start by selecting a product or offer that will serve as your upsell. The key is relevance and value. Ask yourself: What is the next logical thing my customer would want after buying the main product?
Your upsell should complement or enhance the customer’s initial purchase. For example, if the customer bought a laptop, a logical upsell might be a laptop case or an extended warranty.
If they have purchased protein powder, an upsell could be a bundle of protein bars or a discount on the second tub.
2. Map Out Your Funnel Flow (Offers & Sequencing)
Decide how many upsell steps to include and if you’ll offer any downsell. It’s usually best to keep it simple: in many cases 1 or 2 upsell offers are enough, and 3 is the absolute max before it likely irritates customers.
Plan the sequence on paper or a whiteboard. For example: After main purchase, show Upsell Offer #1 (e.g. a premium version of product).
If accepted, then show Upsell Offer #2 (e.g. a related accessory). If Upsell #1 is declined, optionally show a Downsell (a smaller/cheaper offer), then end. This conditional flow ensures the user isn’t bombarded endlessly.
In fact, best practice is that if a customer declines an offer, you show at most one more offer, then stop.
For instance, Bold Commerce’s upsell funnel feature will display one final offer after a decline, then wrap up.
3. Set Up the Upsell Offers on Your Platform
Next you have to implement it. If you use WooCommerce (WordPress), you can use a dedicated plugin to create upsell funnels without coding.
For example, the UpsellWP plugin for WooCommerce allows you to configure one-click upsell offers at multiple points (cart, checkout, post-purchase, etc.) easily.
In UpsellWP, you can set conditions (like which product triggers the upsell), design the offer page, and choose if it appears in a popup, checkout page, or thank-you page.
The main idea is to configure the funnel logic: “If customer buys X, then after purchase show offer Y (Upsell #1); if they accept, then show Z (Upsell #2); if they decline, maybe show W (Downsell)”.
Suggest one-click upsell offers at multiple customer touchpoints using UpsellWP’s upsell campaigns.
4. Craft Compelling Upsell Page Content
Treat your upsell offer page or popup like a mini sales page. A few tips for your upsell offer content:
- Reassure and Transition: First, make sure to confirm their initial purchase on the upsell page (e.g. “Thank you for purchasing [Product]!”). Then smoothly introduce the upsell: “Before you go, here’s a special one-time offer to complement your purchase…”
- Highlight Benefits: Explain how the upsell product will help them even more. For example: “Add this carrying case to protect your new laptop – keep it safe on the go.”
- Make it Exclusive: Create a sense of special opportunity. Many upsell funnels frame the offer as a one-time deal available right now only.
- Use a Clear Call-to-Action: The upsell page typically has two choices: Accept or Decline. Make the “Yes” button prominent (“Yes, add this to my order”) and the “No thanks” link smaller.
5. Implement One-Click Purchase (Optimize the Tech)
The customer should be able to accept the upsell without re-entering payment details.
If you’re custom-building, this typically means tokenizing the payment from the first purchase. One-click upsells dramatically improve conversion because they remove friction.
If one-click isn’t possible, upsells will be much less effective (customers won’t want to fill out a checkout form again for a small add-on).
So, double-check that your setup is truly one-click.
6. Test the Funnel Flow
Before sending real customers through, test the entire upsell funnel yourself (or with a team member). Place a test order for the initial product and go through the upsell offers as if you were a customer. Verify that:
- The correct upsell offer appears at the right time.
- Accepting the upsell adds it to the original order (and charges correctly).
- Declining skips to the proper next step or final page.
- All messaging is clear, and there are no glitches or confusion points.
Make sure the funnel behaves exactly as intended. It’s easier to tweak the logic or wording now than after it’s live.
7. Optimize and Refine
Once your upsell funnel is live, keep an eye on performance. Track the take rate (conversion rate) of each upsell offer.
For instance, if 100 people see Upsell #1, how many click yes? If that number is low, you might need to adjust the offer (maybe the price is too high or the item isn’t enticing).
You can A/B test different upsell offers or copy. Many upsell tools allow split testing of offers to see which one customers prefer.
Also pay attention to any customer feedback; if people are confused or annoyed, you might need to soften the approach (or ensure you’re not showing too many offers).
By following these steps, you can create an effective upsell funnel that works smoothly and boosts your sales. Next, let’s look at some real-world examples to illustrate how upsell funnels function in practice.
Examples of Upsell Funnels in Action
To better understand upsell funnels, let’s explore a few real-world examples from e-commerce businesses. These examples show different types of upsells (and cross-sells) and how they’re implemented.
Example 1: Electronics Store – Camera Purchase Upsell
Imagine a customer buying a digital camera from an online electronics store. As they add the camera to their cart and proceed to checkout, the store triggers an upsell funnel:
- Upsell Offer: On the cart page, a pop-up suggests “Add a 64GB Memory Card for 20% off?” along with a one-click add button. This is a complementary cross-sell offer – the memory card enhances the use of the camera. It’s presented at a crucial point when the customer is about to check out.
- If Accepted: The memory card is added to the cart. Now at checkout, the store presents another offer: “Protect your camera with a 2-Year Extended Warranty for just $49.” This is a true upsell (an enhanced service). The customer can accept with one click, no extra form needed.
- If Declined: If the customer had declined the memory card, the funnel instead show one alternative offer. For example, “How about a Camera Carrying Case at 15% off?” as a last attempt to increase the order value. After that, no further offers are shown if they decline again (to avoid annoyance).
- Outcome: With this funnel, perhaps 30% of customers add the memory card, and 10% add the warranty. The store significantly increases revenue per order. The customer, on the other hand, leaves with a more complete purchase (camera + essential accessories), likely feeling satisfied that they got a deal on useful add-ons.
Example 2: Fashion E-commerce – Apparel Upsell Funnel
Consider an online fashion boutique. A shopper is buying a pair of shoes on the site:
- Upsell Offer: On the checkout page, after entering payment info but before finalizing, a section says: “Complete the Look: Add a pair of premium socks for $5” (perhaps discounted from $8). This is an easy yes for many – socks are low-cost, relevant, and it’s a one-click add. Let’s say many customers take this offer.
- Post-Purchase Upsell: After the order is placed (thank-you page), the store doesn’t say goodbye just yet. Instead, it shows: “Wait – do you need a Shoe Care Kit? Get our polish & brush set 30% off now only $14.” Because the payment is complete, this is a post-purchase upsell that charges their card if they click yes. It appears on the thank-you page as a special one-time offer. Even if only a small fraction of customers accept, it’s extra revenue with zero risk of cart abandonment (since the main purchase is already done).
- Outcome: This funnel effectively used a cross-sell (socks) and an upsell (care kit) to increase AOV. The customer got useful items that genuinely complement their shoes. Many eCommerce stores do this with plugins – for example, showing a “Thank You page upsell” such as offering eco-friendly glass straws after buying a blender, or recommending a tie when someone buys a suit.
Example 3: E-Commerce Store – “Double Your Order” Upsell
This example comes from a WooCommerce plugin scenario (like one offered by UpsellWP):
- A customer has added a bottle of gourmet hot sauce to their cart, priced at $10.
- Upsell Offer (Checkout): At checkout, an offer section highlights “Get a second bottle for 50% off – stock up and save!” with a one-click add. This “Double the Order” upsell encourages the customer to buy more of the same item at a discount. It plays on the idea that if they like the product, why not get two and save money.
- If Declined: Suppose the customer says no to the second bottle. After completing the purchase, on the thank-you page the site might try one more time with a downsell: “Maybe try our mild version as well for just $8? (special offer).” This is a different product (cross-sell) at a slightly lower price, as a last attempt.
- Outcome: A portion of customers will accept one of these offers. The business effectively increases each order’s value; some customers end up buying two bottles, others add on a different flavor.
From the merchant’s perspective, the plugin handles adding the item to the existing order and charging the card. The result is a higher average order value without any manual effort.
These examples show how versatile upsell funnels can be. Also notice how the number of offers is kept reasonable (usually one or two follow-ups) to avoid frustrating the buyer.
Get started with UpsellWP’s double the offer campaign and increase your average order value easily.
Final Words
Upsell funnels are one of the most underrated ways to grow revenue fast. Done right, they improve AOV, boost retention, and give customers more value.
Start small. Think about what else your customers need after their first purchase – then guide them there. Tools like UpsellWP make it easy to build these high-converting flows without friction.
Frequently Asked Questions
A sales funnel is the journey customers take from first hearing about your product to making a purchase. It visualizes how prospects move through stages like awareness, interest, consideration, and finally conversion into paying customers.
An upsell strategy involves offering customers a higher-value or premium version of their chosen product. It increases revenue per customer by suggesting upgrades, add-ons, or enhanced features that provide additional value.
Yes, sales funnels work effectively when properly designed and implemented. They help businesses systematically guide prospects through the buying process, increase conversion rates, and identify where potential customers drop off for optimization.
The five stages are: Awareness (attracting prospects), Interest (engaging potential customers), Consideration (evaluating options), Intent (showing purchase readiness), and Purchase (completing the transaction).
The seven steps are: Prospecting (finding leads), Preparation (researching prospects), Approach (initial contact), Presentation (demonstrating value), Handling objections, Closing the sale, and Follow-up (maintaining relationships and seeking referrals).